Hazards Above: Part 2
Monday, July 19th, 2010My last post, Hazards Above, provided a brief overview of three incidents involving extreme fire behavior in the attic or truss loft void spaces of wood frame dwellings. This post will examine the similarities and differences between these lessons and identify several important considerations when dealing with fires occurring in or extending to void spaces. At the conclusion of Hazards Above, I posed five questions:
- What is similar about these incidents and what is different?
- Based on the limited information currently available, what phenomena do you think occurred in each of the cases? What leads you to this conclusion?
- What indicators might have pointed to the potential for extreme fire behavior in each of these incidents?
- How might building construction have influenced fire dynamics and potential for extreme fire behavior in these incidents?
- What hazards are presented by fires in attics/truss lofts and what tactics may be safe and effective to mitigate those hazards?
Similarities and Differences
The most obvious similarities between these incidents was that the buildings were of wood frame construction, the fire involved or extended to an attic or truss loft void space, and that some type of extreme fire behavior occurred. In two of the incidents firefighters were seriously injured, while in the other firefighters escaped unharmed.
Given the limited information available from news reports and photos taken after the occurrence of the extreme fire behavior events, it is not possible to definitively identify what types of phenomena were involved in these three incidents. However, it is interesting to speculate and consider what conditions and phenomena could have been involved. It might be useful to examine each of these incidents individually and then to return to examine fire behavior indicators, construction, and hazards presented by these types of incidents.
Minneapolis, MN
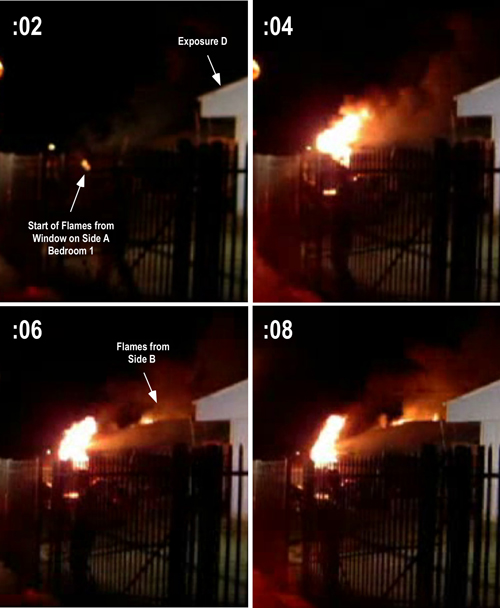
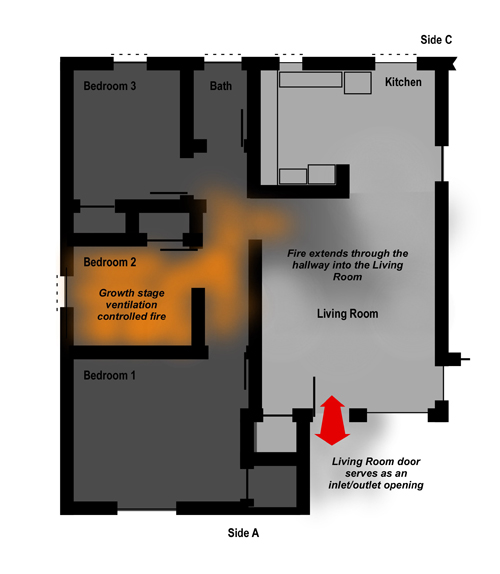
In the Minneapolis incident the fire occurred in an older home with legacy construction and relatively small void spaces behind the knee walls and above the ceiling on Floor 3. The triggering event for the occurrence of extreme fire behavior is reported to be opening one of the knee walls on Floor 3. As illustrated in Figure 1, the fire appeared to transition quickly to a growth stage fire (evidenced by the dark smoke and bi-directional air track from the windows on Floor 3 Side A. However blast effects on the structure are not visible in the photo and were not reported.
Figure 1. Minneapolis MN Incident: Conditions on Side A
Note: Photo by Steve Skar
Potential Influencing Factors: While detail on this specific incident is limited, it is likely that the fire burning behind the knee wall was ventilation controlled and increased ventilation resulting from opening the void space resulted in an increase in heat release rate (HRR). Potential exists for any compartment fire that progresses beyond the incipient stage to become ventilation controlled. This is particularly true when the fire is burning in a void space.
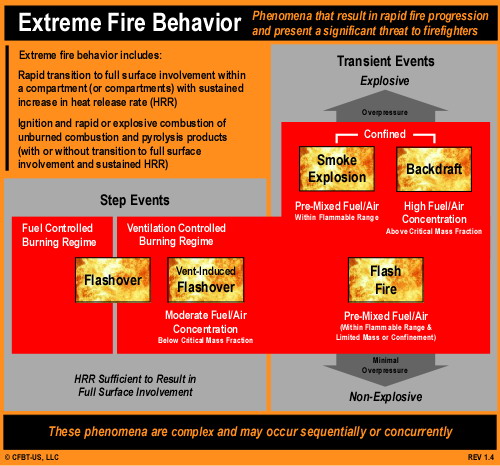
Extreme Fire Behavior: While statements by the fire department indicate that opening the knee wall resulted in occurrence of flashover, this is only one possibility. As discussed in The Hazard of Ventilation Controlled Fires and Fuel and Ventilation, increasing ventilation to a ventilation controlled fire will result in increased HRR. Increased HRR can result in a backdraft (if sufficient concentration of gas phase fuel is present), a vent induced flashover, or simply fire gas ignition (such as rollover or a flash fire) without transition to a fully developed fire.
Harrisonburg, VA
The Harrisonburg incident involved extreme fire behavior in Exposure D (not the original fire unit). The extreme fire behavior occurred after members had opened the ceiling to check for extension. However, this may or may not have been the precipitating event. As illustrated in Figure 2, as members prepare to exit from the windows on Floor 3 , Side C, flames are visible on the exterior at the gable, but it appears that combustion is limited to the vinyl siding and soffit covering. There are no indicators of a significant fire in Exposure D at the time that the photo was taken. However, it is important to remember that this is a snapshot of conditions at one point in time from a single perspective.
Figure 2. Harrisonburg, VA Incident: Conditions on Side C
Note: Photo by Allen Litten
Potential Influencing Factors: The truss loft was likely divided between units by a 1 hour fire separation (generally constructed of gypsum board over the wood trusses). While providing a limited barrier to fire and smoke spread, it does not generally provide a complete barrier and smoke infiltration is likely. Sufficient smoke accumulation remote from the original fire location can present risk of a smoke explosion (see NIOSH Report 98-03 regarding a smoke explosion in Durango, Colorado restaurant). Alternately, fire extension into the truss loft above an exposure unit can result in ventilation controlled fire conditions, resulting in increased HRR if the void is opened (from above or below).
Extreme Fire Behavior: Smoke, air track, and flame indicators on Side C indicate that the fire in the truss loft may not have continued to develop past the initial ignition of accumulated smoke (fuel). It is possible that smoke accumulated in the truss loft above Exposure B and was ignited by subsequent extension from the fire unit. Depending on the fuel (smoke)/air mixture when flames extended into the space above Exposure B ignition could have resulted in a smoke explosion or a less violent fire gas ignition such as a flash fire.
Sandwich, MA
In the Sandwich incident, the extreme fire behavior occurred shortly after the hose team applied water to the soffit. However, this may or may not have been the precipitating event. As illustrated in Figure 3, the fire transitioned to a fully developed fire (likely due to the delay in suppression as the injured members were cared for). Blast effects on the structure are obvious.
Figure 3: Sandwich, MA: Conditions on Sides C and D
Note: Photos by Britt Crosby (http://www.capecodfd.com)
Potential Influencing Factors: The roof support system in this home appears to have been constructed of larger dimensional lumber (rather than lightweight truss construction). In addition, it is likely that the attic void spaces involved in this incident were large and complex (given the size of the dwelling and complex roof line). It appears that at least part of the home had a cathedral ceiling. Fire burning in the wood framing around the metal chimney would have allowed smoke (fuel) and hot gases to collect in the attic void in advance of fire extension.
Extreme Fire Behavior: The violence of the explosion (see blast damage to the roof on Side D in Figure 3) points to the potential for ignition of pre-mixed fuel (smoke) and air, resulting in a smoke explosion. However, it is also possible that failure of an interior ceiling (due to water or steam production from water applied through the soffit) could have increased ventilation to a ventilation controlled fire burning in the attic, resulting in a backdraft).
Fire Behavior Indicators
The information provided in news reports points to limited indication of potential for extreme fire behavior. One important question for each of us is how we can recognize this potential, even when indicators are subtle or even absent.
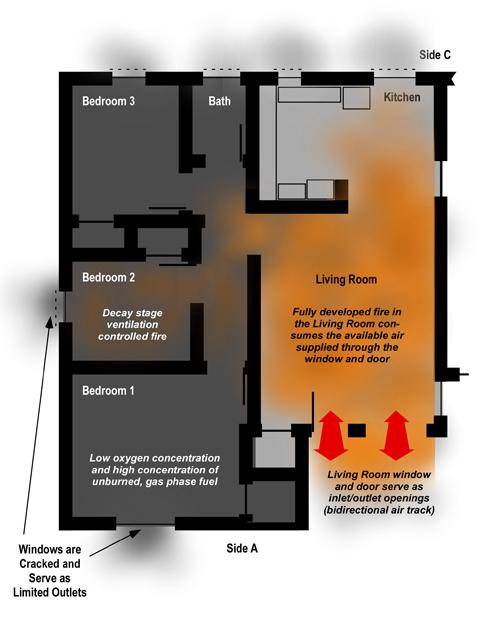
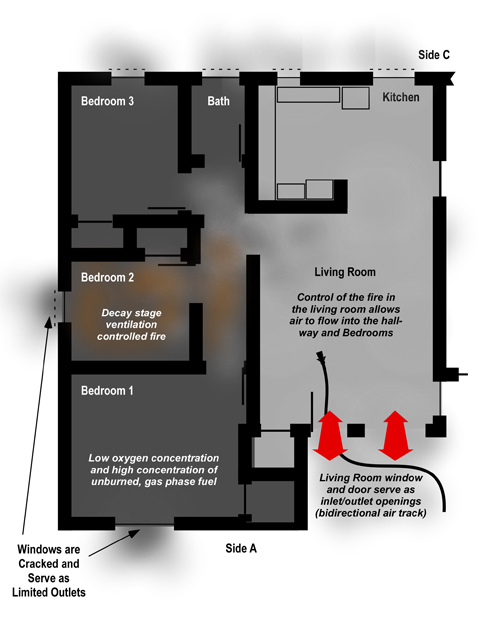
Important! A growth stage fire can present significant smoke and air track indicators, with increasing thickness (optical density), darkening color, and increasing velocity of smoke discharge. However, as discussed in The Hazard of Ventilation Controlled Fires, when the fire becomes ventilation controlled, indicators can diminish to the point where the fire appears to be in the incipient stage. This change in smoke and air track indicators was consistently observed during the full-scale fire tests of the influence of ventilation on fires in single-family homes conducted by UL earlier this year.
Even with an opening into another compartment or to the exterior of the building, a compartment fire can become ventilation controlled. Consider building factors including potential for fire and smoke extension into void spaces in assessing fire conditions and potential for extreme fire behavior. A ventilation controlled fire or flammable mixture of smoke and air may be present in a void space with limited indication from the exterior or even when working inside the structure.
Building Construction
Each of these incidents occurred in a wood frame structure. However, the construction in each case was somewhat different.
In Minneapolis, the house was likely balloon frame construction with full dimension lumber. As with many other structures with a “half-story”, the space under the pitched roof is framed out with knee walls to provide finished space. This design is not unique to legacy construction and may also be found with room-in-attic trusses. The void space behind the knee wall provides a significant avenue for fire spread. When involved in fire, opening this void space can quickly change fire conditions on the top floor as air reaches the (likely ventilation controlled) fire.
The incident in Harrisonburg involved a fire in a townhouse with the extreme fire behavior phenomena occurring in an exposure. While not reported, it is extremely likely that the roof support system was comprised of lightweight wood trusses. In addition, there was a reverse gable (possibly on Sides A and C) that provided an additional void. As previously indicated, the truss loft between dwelling units is typically separated by a one-hour rated draft stop. Unlike a fire wall, draft stops do not penetrate the roof and may be compromised by penetrations (after final, pre-occupancy inspection). Installed to code, draft stops slow fire spread, but may not fully stop the spread of smoke (fuel) into the truss lofts above exposures.
Firefighters in Sandwich were faced with a fire in an extremely large, wood frame dwelling. While the roof appeared to be supported by large dimensional lumber, it is likely that there were large void spaces as a result of the complex roofline. In addition, the framed out space around the metal chimney provided an avenue for fire and smoke spread from the lower level of the home to the attic void space.
Hazards and Tactics
Forewarned is forearmed! Awareness of the potential for rapid fire development when opening void spaces is critical. Given this threat, do not open the void unless you have a hoseline in hand (not just nearby).
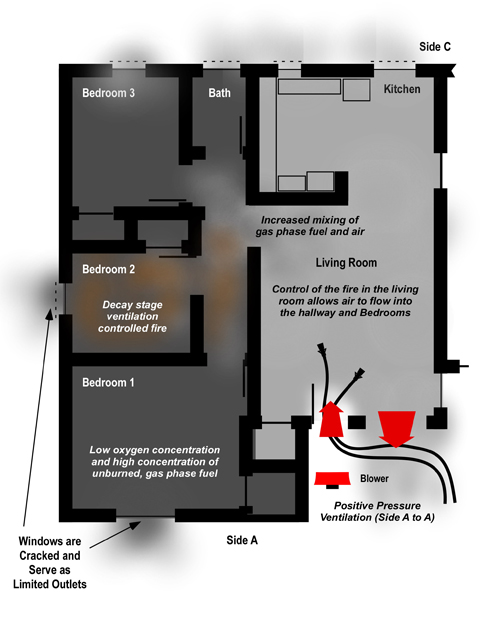
Indirect attack can be an effective tactic for fires in void spaces. This can be accomplished by making a limited opening and applying water from a combination nozzle or using a piercing nozzle (which further limits introduction of air into the void).
If there are hot gases overhead, cool them before pulling the ceiling or opening walls when fire may be in void spaces. Pulses of water fog not only cool the hot gases, but also act as thermal ballast; reducing the potential for ignition should flames extend from the void when it is opened.
Lastly, react immediately and appropriately when faced with worsening fire conditions. Review my previous posts on Battle Drill (Part 1, Part 2, and Part 3). An immediate tactical withdrawal under the protection of a hoseline is generally safer than emergency window egress (particularly when ladders have not yet been placed to the window).
Ed Hartin, MS, EFO, MIFireE, CFO