NIOSH Firefighter Fatality Investigation & Prevention:
Part 2
Monday, November 17th, 2008
This post is a continuation of my feedback to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health that will be presented at the public stakeholder meeting conducted in Chicago, IL on 19 November 2008. My recommendations are presented in the form of an analysis of NIOSH Report F2007-29. This incident resulted in the death of Captain Kevin Williams and Firefighter Austin Cheek of the Noonday Volunteer Fire Department.
This post continues with discussion the NIOSH reports examination of the influence of ventilation in this incident and provides specific recommendations for improvement of the NIOSH Firefighter Fatality Investigation and Prevention Program.
Tactical Ventilation
The NIOSH report makes a general recommendation that “fire departments should ensure that properventilation is done to improve interior conditions and is coordinated with interior attack”ť [emphasis added]. However, the report is misleading and fails to address key issues related to tactical ventilation, its effective application, and its tremendous influence fire behavior.
NIOSH Report F2007-29 indicated that positive pressure ventilation was initiated prior to the second entry by the initial attack crew (a significant difference from the information provided in the Texas State Fire Marshal’s report). However, no mention is made of any action (or lack thereof) to create an adequate exhaust opening for effective horizontal positive pressure ventilation. While advising that ventilation needs to be proper, it would be helpful to provide more specific guidance. Lack of an adequate exhaust opening prior to pressurizing the building has been a major factor in a number of incidents in which application of positive pressure resulted in extreme fire behavior such as ventilation induced flashover or backdraft. Positive Pressure Attack for Ventilation and Firefighting (Garcia, Kauffmann, & Schelble, 2006), Fire Ventilation (Svensson, 2000), and Essentials of Firefighting (IFSTA, 2008) all emphasize the importance of creating an adequate exhaust opening prior to application of positive pressure.
The NIOSH report pointed out that smoke pushed out the inlet and overrode the effects of the blower, but attributed this to the presence of an attic floor that interfered with vertical ventilation rather than the lack of an adequate exhaust opening for the initial horizontal ventilation.
The PPV fan and vertical ventilation had little effect due to an attic floor being installed. At 0231 Chief #2 had horizontally vented the window on the D side near the A/D corner.
In this incident, ventilation was being performed while the interior attack crew was already inside working. When the ventilation was completed, minimal smoke was pushed out of the vented hole but dark smoke pushed out of the front door, in spite of the fact that a PPV fan was set up at the front door. Note: The dark smoke pushing out the door indicated that the conditions were worsening and the vertical ventilation was not impacting the fire.
In addition, the report fails to note that the opening made on Side D near the AD Corner placed the attack team between the fire and an exhaust opening. As with lack of an adequate exhaust opening, this has been demonstrated to have the potential for disastrous consequences (see NIOSH Death in the Line of Duty F2004-02).
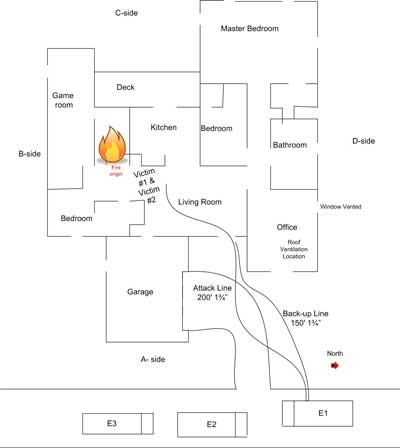
Floor Plan Illustrating the Position of Captain Williams and Firefighter Cheek
Texas State Fire Marshal’s Office Firefighter Fatality Investigation Report FY 07-02
Extreme Fire Behavior
Command ordered companies to abandon the building at 0234 hours using three air horn blasts as an audible signal. The NIOSH report indicated that heavy fire “continued to roll out the front door”ť but it is unclear how soon this occurred after smoke conditions at the doorway changed.
NIOSH Report F2007-29 does not clearly identify that extreme fire behavior was a causal or even contributory factor in the deaths of Captain Williams and Firefighter Cheek. It simply states that they died as a result of smoke inhalation and thermal burns.
NIOSH Recommendations
NIOSH made six recommendations based on analysis of the incident in which Captain Williams and Firefighter Cheek lost their lives. Several of these recommendations focused on factors that may have contributed to these two LODD. These included radio communications equipment and procedures, accountability, rapid intervention, and the importance of mutual aid training. Two recommendations were more directly related to causal factors: The importance of ongoing risk assessment and use of proper and coordinated ventilation. However, these broad recommendations miss the mark in providing useful guidance in minimizing the risk of similar occurrences.
Ensure that the IC conducts a risk-versus-gain analysis prior to committing to interior operations and continue the assessment throughout the operation.
This statement is necessary but not sufficient. Size-up and risk assessment is not only the responsibility of the incident commander. All personnel on the fireground must engage in this process within the scope of their role and assignment. Understanding practical fire dynamics is critical to firefighters’ and fire officers’ ability to recognize what is happening and predict likely fire behavior and the influence of tactical operations. To effectively address this issue, NIOSH death in the line of duty reports must be explicit and detailed with regards to key fire behavior indicators observed, subsequent fire behavior phenomena, and the influence of the action or inaction of responders on fire development.
Fire departments should ensure that proper ventilation is coordinated with interior attack.
NIOSH Report 2007-29 focused on the ineffectiveness of the vertical ventilation, but failed to recognize the impact of the sequence of action (i.e. pressurization of the building and creation of exhaust openings), inadequacy of initial exhaust openings, and eventual location of exhaust openings in relation to the operating position of Captain Williams and Firefighter Cheek.
As with situational awareness, effective tactical operations are grounded in training, education, and experience. The incident commander and crews tasked with carrying out tactical ventilation must understand how these tactics influence the fire environment and fire behavior. As with size-up and risk assessment, this is dependent on an understanding of practical fire dynamics.
Other than indicating that ventilation must be coordinated with interior attack, the NIOSH report did not speak to fire control operations conducted during this incident. From the building floor plan and information presented in both the reports by NIOSH and the Texas State Fire Marshal, it appears that the fire was shielded and direct attack was not possible from the position of the first attack team nor the position reached by Captain Williams and Firefighter Cheek. The Fire Marshal’s report indicated that the initial attack team “penciled”ť the ceiling to control flames overhead and experienced disruption of the hot gas layer and an increase in temperature at floor level.
Just as ventilation must be appropriate and coordinated with interior fire attack, fire control must also be appropriate and coordinated with tactical ventilation. Cooling the hot gas layer is an appropriate tactic to create a buffer zone and increase the safety of the attack team as they access a shielded fire. However, penciling (use of an intermittent application of a straight stream) the ceiling is an ineffective method of cooling the hot gas layer and results in excessive steam production. In addition, cooling the hot gas layer is not an extinguishment technique; it must be integrated with other fire control methods such as a direct attack on the seat of the fire.
NIOSH death in the line of duty reports must explicitly address the effect of tactical operations, particularly where effectiveness or ineffectiveness was a contributing or causal factor in the LODD.
The Way Forward
While this assessment has been quite critical of NIOSH’s investigation of traumatic fatalities involving extreme fire behavior, it is important to emphasize that with all its faults, the Firefighter Fatality Investigation and Prevention program is a tremendous asset to the fire service.
The following recommendations are made to further strengthen and improve the quality of this program and the utility of recommendations made to reduce the risk of firefighter line of duty deaths as a result of extreme fire behavior during structural firefighting operations:
- Emphasize the criticality of understanding fire behavior, causal factors in extreme fire behavior, and the influence of tactical operations such as fire control and ventilation.
- Increase attention to building, smoke, air track, heat, and flame indicators when investigating incidents which may have involved extreme fire behavior as a causal or contributing factor in LODD.
- Examine training in greater detail, with specific emphasis on fire behavior, situational assessment, realistic live fire training, and crew resource management.
- Provide fire behavior training to all NIOSH investigators to improve their understanding of fire development, extreme fire behavior phenomena, and the impact of tactical operations.
- Include a fire behavior specialist on the investigation team when investigating incidents that may have involved extreme fire behavior as a causal or contributing factor.
- Initiate investigations quickly to avoid degradation of the quality of information obtained from the individuals involved in the incident and other witnesses.
Ed Hartin, MS, EFO, MIFireE, CFO
References
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). (2008). Death in the line-of-duty… Report 2007-29. Retrieved November 14, 2008 from NIOSH http://www.cdc.gov/NIOSH/FIRE/reports/face200729.html.
Texas State Fire Marshal’s Office (2008). Firefighter fatality investigation FY 07-02. Retrieved November 14, 2008 from http://www.tdi.state.tx.us/reports/fire/documents/fmloddnoonday.pdf
Svensson, S. (2000). Fire ventilation. Karlstad, Sweden: Swedish Rescue Services Agency
Garcia, K., Kauffmann, R., & Schelble, R. (2006). Positive pressure attack for ventilation & firefighting. Tulsa, OK: Pen Well
International Fire Service Training Association. (2008) Essentials of Firefighting (5th ed). Stillwater, OK: Fire Protection Publications.